Sleep Apnea

The Definition and Symptoms of Sleep Apnea, is a breathing disorder occurring during sleep where an individual has recurrent episodes of stopping breathing (apneas) for short periods of time (10-30 seconds or more). These apneic episodes may occur as often as 20 to 100 times per hour in individuals with severe sleep apnea. These episodes typically occur as one’s muscles relax while asleep and their tongue falls to the back of the throat or one’s throat tissue collapses while breathing in (obstructive sleep apnea). Apneas may also occur as a result of a disturbance in the brain’s breathing center (central sleep apnea). Sleep apnea is believed to affect at least 1-2% of the adult population, particularly males age 30-60 years of age, but realize it is also seen in children and women. This sleep disorder is a serious problem. Even though a person may not know they stop breathing at night, repeated apneic events cause disruptions of normal sleep. As a result of these disruptions, individuals become sleep deprived leading to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, irritability, memory loss, and lack of energy. Furthermore, life-threatening reductions in blood oxygen level as well as heart beat irregularities may occur during these apneic events. It is also well known that apnea causes high blood pressure, early heart attacks and strokes. Three common characteristics found in individuals with obstructive sleep apnea include being overweight or having a pear shaped abdomen, being a loud snorer, and being sleepy or fatigued. Snoring alone is a common finding in the general population, occurring in about 10-30% of all people. Not everyone who snores has obstructive sleep apnea. Individuals who snore loudly, however, and complain of persistent sleepiness, warrant evaluation by a sleep physician. A sure sign of having apnea is having a cyclical snoring pattern followed by quiet or silent periods (apneic periods), which are then followed by a snorting or grunting episode as well as kicking or movement in bed (an arousal event). Because individuals with sleep apnea are not awake and therefore are not aware of their sleep behavior, it is often the bedpartner leading the person to seek medical attention as they observe this pattern of abnormal breathing during sleep. The only symptom sleep apneics may realize is not feeling refreshed in the morning or always sleepy. Another feature for individuals with sleep apnea is falling asleep easily during inactive tasks such as watching television, reading, sitting in church or listening to a boring lecture, or even at inappropriate times such as while at work, driving an automobile, or even while carrying on conversation with another person. Individuals may also experience morning headaches, a dry or sore throat upon awakening, forgetfulness, difficulty with concentration, being depressed, anxious or irritable.
Proper treatment of sleep apnea may prevent or reverse the potentially life threatening consequences. The diagnosis of sleep apnea requires an evaluation by a physician who recognizes the symptoms found in sleep apnea. An individual suspected to have apnea should then undergo an overnight sleep study to evaluate their breathing pattern, blood oxygen level, and heartbeat during sleep. The number of times a person stops breathing per hour, the duration of these events, and the affect they have on one’s oxygen and heart help determine the severity of the apnea. A physician specializing in sleep medicine can decide whether a sleep test can be performed in your home or should be performed in a sleep laboratory setting.Treatment of sleep apnea is individualized and depends on the disease severity. General measures include weight loss, avoidance of alcohol or sleeping pills before bedtime, and treatment of any sinus problems. A positional device can be worn, or slept with which is used to help minimize sleeping on one’s back, a position where apnea is often worse. Dentists and other health professionals are also recommending specially fitted oral devices which can be very effective in the treatment of some patients with apnea or snoring.In the more severe cases of sleep apnea, a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device is typically recommended for use. The CPAP device includes a nasal mask which the person wears to bed. This device provides a gentle column of air to the upper throat that acts to keep the airway open during sleep, preventing tissue collapse and eliminating both snoring and apnea. The amount of air pressure required to treat sleep apnea will vary for different individuals. The treatment is very effective, but an adjustment period may be needed to get use to wearing the CPAP machine. In selected individuals not treatable by the above measures, surgical approaches may be useful. Surgical options include correcting sinus disease or removal of soft tissues in the back of the throat such as the uvula, soft palate, and tonsils (uvulopalatopharygoplasty).It is important to realize that sleep apnea is a common disorder, that if untreated, may lead to poor health, persistent sleepiness and fatigue, social and psychological problems, and an increased risk of injury related to falling asleep while driving or in dangerous situations. If you suffer from loud snoring, have restless sleep with associated grunting or choking sensations, have daytime fatigue, or a bedpartner has observed episodes in which you may have stopped breathing, consider a complete evaluation by a health professional who is experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea.
Sleep Apnea in Columbus
Sleep Apnea in Phenix City
Sleep Apnea and Hypertension
KNOW...About Sleep Apnea and Hypertension...
- Sleep Apnea is associated with significant risk of HTN even after controlling for known confounding parameters
- Sleep Apnea leads to HTN in a dose-response relationship
- 83% of Refractory Hypertension patients have significant Sleep Apnea
- JNC7 recognizes Sleep Apnea as an important cause of hypertension
- A large percentage of these patients remain undiagnosed
ASK...HTN patients a few simple questions on how they sleep...
- Do you snore?
- Do you wake to urinate? How many times?
- Do you feel tired after sleeping?
- Do you fall asleep during mundane activities? (reading, watching TV)
REALIZE...Positive outcomes when diagnosed Sleep Apnea is treated w/CPAP...
- Reduced daytime BP in Apnea patients
- Effectively reduced systolic BP in refractory HTN patients w/OSA
- Normalized nocturnal BP pattern in non-dipper OSA population
- Reduced the need for anti-hypertensive drugs in patients with refractory HTN
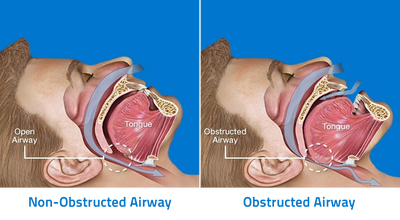
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is caused by the closing of the upper airway while asleep. OSA causes a drop in one’s blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) and an increase in the blood’s carbon dioxide (CO2). When the SaO2 drops the heart will start pumping more blood with each beat. If the SaO2 continues to drop the heart will start beating faster and faster. As the CO2 increases the brain will try to drive the person to breathe. The effort and the action of the abdomen and chest will increase. Eventually that action can become severe enough to cause the individual to stir or awaken in an effort to clear the upper airway blockage, allowing the person to breathe. Then go back to sleep, where the same thing will happen again and again.
How is OSA Diagnosed
Diagnosis of OSA is made by a physician specially trained in sleep medicine. If it is determined that the patient might have asleep disorder, they would be asked to take a polysomnogram (sleep study). This sleep study will monitor several sleep parameters including EEG, EKG, eye movement, chin movement, air flow, chest efforts, abdomen, SaO2, snoring and leg movement. Each parameter serves to help the physician make a correct diagnosis.
Treatment of OSA
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) appears to be the best and most effective treatment for OSA. CPAP flow generators develop a constant, controllable pressure to keep your upper airway open, allowing the patient to breathe normally. CPAP is effective on 95% of the patients diagnosed with OSA. These units are reliable, quiet and efficient and come in a variety of sizes and shapes.
Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies. By continuing to use this site, you accept our use of cookies.